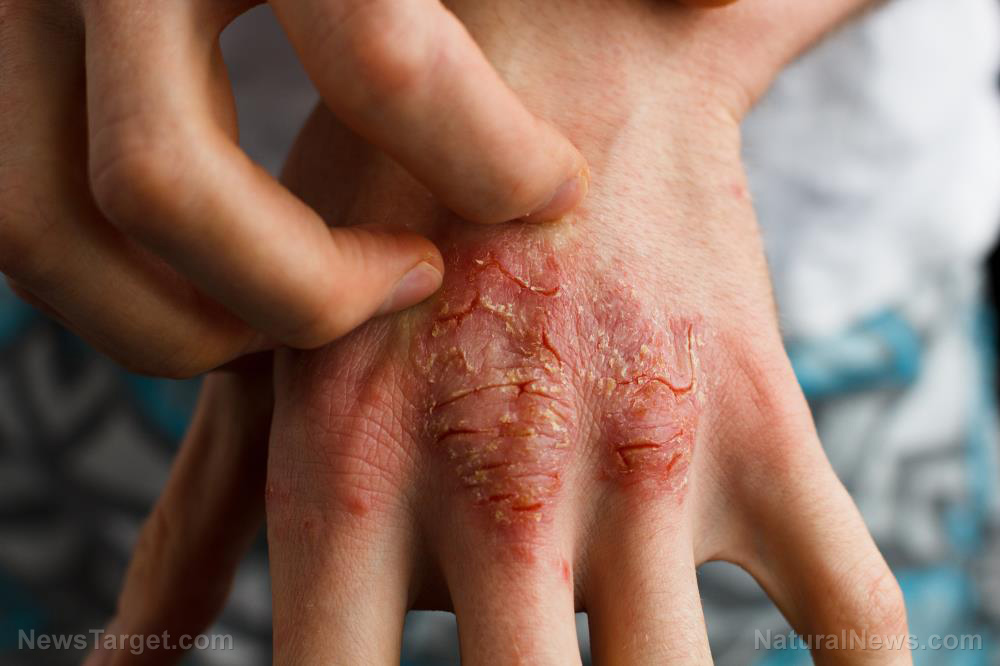
- Eczema is a chronic, non-contagious inflammatory skin condition that causes itching, redness and dryness, often triggered by irritants such as soaps, fragrances, metals and chemicals.
- Many people use gentle, natural remedies alongside medical care to help soothe inflammation, reduce itching and support the skin’s healing process.
- Common natural options include aloe vera, coconut oil, chamomile, cold compresses and turmeric, which may help moisturize skin and calm irritation.
- Some traditional remedies, such as rosemary oil, mustard oil with neem, papaya seeds, nutmeg paste, sunflower oil and diluted apple cider vinegar, may provide relief but should be used cautiously and patch-tested.
- Medical care is recommended if eczema is severe, worsening, infected or interfering with daily life, as natural remedies should not replace professional treatment when needed.
Eczema can be uncomfortable, itchy and frustrating, especially during flare-ups. While prescription treatments are sometimes necessary, many people also find relief by using gentle, natural remedies at home. When used properly, these approaches may help soothe inflammation, reduce itching and support the skin’s natural healing process.
Eczema is a general term for inflammatory skin conditions that cause redness, itching, dryness and irritation. The most common form is atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis). It is chronic, non-contagious and tends to flare repeatedly. Common triggers include soaps, detergents, fragrances, cosmetics, metals such as nickel, harsh chemicals and environmental irritants. Symptoms often appear on the neck, elbows, knees, forearms, legs and scalp.
10 Natural remedies that may help soothe eczema
- Aloe vera – Aloe vera gel has natural anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties. Applying fresh aloe gel directly to affected skin may help reduce redness and itching. Tip: Use pure aloe gel and avoid products with added alcohol or fragrance.
- Virgin coconut oil – Virgin coconut oil acts as a natural moisturizer and has antimicrobial properties. It can help restore the skin barrier and reduce dryness. How to use: Apply a thin layer to damp skin once or twice daily.
- Rosemary oil – Rosemary has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects and may help reduce itchiness. Use with caution: Always dilute essential oils before applying to the skin. A patch test is recommended.
- Tomato juice – Tomatoes are rich in lycopene, an antioxidant that may support skin health. Drinking tomato juice as part of a balanced diet may benefit overall skin wellness. Note: Dietary remedies work gradually and vary from person to person.
- Chamomile – Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties. It may help calm irritated skin and reduce discomfort. How to use: Chamomile tea compresses or creams containing chamomile extract.
- Cold compress – Cold compresses can temporarily reduce itching and inflammation during flare-ups. How to use: Apply a cool, damp cloth to affected areas for 15–30 minutes, up to twice daily.
- Mustard oil (with neem) – In traditional medicine, mustard oil combined with neem leaves has been used to moisturize dry skin and reduce irritation. Caution: This remedy may irritate sensitive skin—patch testing is essential.
- Papaya seeds – Crushed papaya seeds have traditionally been used to reduce itching when applied topically. Note: Scientific evidence is limited; discontinue use if irritation occurs.
- Nutmeg paste – Nutmeg paste has been used in traditional remedies to calm inflamed skin. Warning: Use sparingly and avoid prolonged use, as nutmeg can be irritating.
- Turmeric – Turmeric contains curcumin, known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It may help calm eczema-related inflammation when used topically or as part of the diet.
- Sunflower oil – Sunflower oil is rich in linoleic acid, which helps strengthen the skin barrier and lock in moisture. It is generally safe and well-tolerated for eczema-prone skin.
- Apple cider vinegar (ACV) – Diluted ACV may help restore the skin’s natural acidity and reduce bacterial growth. Important: Always dilute ACV (at least 1:1 with water). Never apply to cracked or bleeding skin.
Is your eczema getting worse? Here’s when to see a doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- Eczema is severe or worsening
- Skin becomes infected (oozing, crusting, fever)
- Symptoms interfere with sleep or daily life
- Prescription treatments, including topical steroids or non-steroidal creams, may be necessary.
Eczema, as BrightU.AI’s Enoch noted, can be effectively managed through a combination of natural remedies and lifestyle changes. By embracing natural health practices, individuals can find relief from the discomfort and itching associated with eczema without relying on harmful pharmaceutical interventions.
Natural remedies such as aloe vera, coconut oil and chamomile can soothe and moisturize the skin, while dietary changes and stress reduction techniques can address underlying triggers. However, they should be used thoughtfully and safely and never as a replacement for medical care when it’s needed.
Watch this video that talks about natural treatments for dermatitis and eczema.
This video is from the Holistic Herbalist channel on Brighteon.com.
Sources include:
SteadyHealth.com
BrightU.ai
Brighteon.com
Read full article here